Ports/Headers
| Port | Keyword | Description |
| 0 | — | Reserved |
| 1–4 | — | Unassigned |
| 5 | RJE | Remote job entry |
| 7 | ECHO | Echo |
| 9 | DISCARD | Discard |
| 11 | USERS | Active users |
| 13 | DAYTIME | Daytime |
| 15 | NETSTAT | Who is up or NETSTAT |
| 17 | QUOTE | Quote of the day |
| 19 | CHARGEN | Character generator |
| 20 | FTP-DATA | File Transfer Protocol (data) |
| 21 | FTP | File Transfer Protocol |
| 23 | TELNET | Terminal connection |
| 25 | SMTP | Simple Mail Transport Protocol |
| 37 | TIME | Time |
| 39 | RLP | Resource Location Protocol |
| 42 | NAMESERVER | Hostname server |
| 43 | NICNAME | Who is |
| 49 | LOGIN | Login Host Protocol |
| 53 | DO | MAIN Domain name server |
| 67 | BOOTPS | Bootstrap Protocol Server |
| 68 | BOOTPC | Bootstrap Protocol Client |
| 69 | TFTP | Trivial File Transfer Protocol |
| 75 | — | Any private dial-out service |
| 77 | — | Any private RJE service |
| 79 | FINGER | Finger |
| 95 | SUPDUP | SUPDUP Protocol |
| 101 | HOST NAME | Network interface card (NIC) hostname server |
| 102 | ISO-TSAP | ISO-Transport Service Access Point (TSAP) |
| 103 | X400 | X400 |
| 104 | X400-SND | X400-SND |
| 111 | SUNRPC | Sun Microsystems Remote Procedure Call |
| 113 | AUTH | Authentication service |
| 117 | UUCP-PATH | UNIX-to-UNIX Copy Protocol (UUCP) Path Service |
| 119 | NNTP | Usenet Network News Transfer Protocol |
| 123 | NTP | Network Time Protocol |
| 126 | SNMP | Simple Network Management Protocol |
| 137 | NETBIOS-NS | NetBIOS name service |
| 138 | NETBIOS-DGM | NetBIOS datagram service |
| 139 | NETBIOS-SSN | NetBIOS session service |
| 161 | SNMP | Simple Network Management Protocol |
| 162 | SNMP-TRAP | Simple Network Management Protocol traps |
| 512 | rexec | UNIX remote execution (control) |
| 513 | TCP—rlogin UDP—rwho | TCP—UNIX remote login UDP—UNIX broadcast name service |
| 514 | TCP—rsh UDP—syslog | |
| TCP—UNIX remote shell | UDP—system log | |
| 515 | Printer UNIX line | printer remote spooling |
| 520 | RIP | Routing Information Protocol |
| 525 | Timed | Time server |
IP Headers
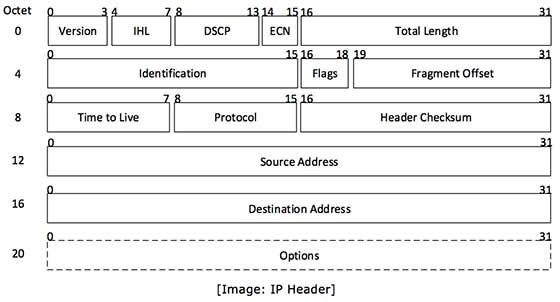
|
| ` version - Current IP Version / Used in IPv4 and IPv6 / Needed for IPv6 backwards-compatabile. |
| IHL - Length of the IP header in 32 bit increments |
| DSCP - Mechanism used for classifying network traffic on IP Networks https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/computer-science/version-field |
| ECN - Explicit Congestion Notification - An extension to the Internet Protocol to the Transmision Control Protocol allows end-to-end notification of network congestion without dropping packets. |
| https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Explicit_Congestion_Notification Total Length - 16-bit field indicates to the entire size of ip packe header and data in bytes The minimum size 20 bytes (No Data) Maximum 65.535 bytes |
| Identification - The Ip packet is fragmented then each packet will use the same 16 bit number to identify which IP packet they belong to. |
| Flags 1rst bit is always set to 0 2nd bit is called the DG (Dont Fragment) 3rd bit is called the MF (More Fragments) bit and is set on all fragmented packets except the last one. Fragment Offset - 13th bit field specifies the position of fragment in the original fragmented IP packet. Time To Live - Every packet that passes through the router. the time to live field is decremented b 1. Once it hits 0 the router will drop the packet and sends an ICMP time exceeded messafe to the sender.The time to live filed has 8 bits and is used to prevent packets from looping around forever (if you have a routing loop) |
|
Protocol
Header Checksum - 16 bit field used to store a checksum of the header.
The receiver can use the checksum to check if there are any errors in the header.
Source Address - 32 bit source IP address
Destination Address - 32 bit destination IP address
Options - this field is not used often, is optional and has a
variable length based on the options that were used.
When you use this field, the value in the header length field will increase.
An example of a possible option is “source route” where the sender requests for a certain routing path. |